Lupus is a disorder, an auto-immune one, where the immune system attacks its own cells. This leads to inflammation, tissue damage and a lot of pain. Lupus can affect many body systems – kidneys, blood, joints, lungs, heart etc and can be a difficult one to diagnose, as its signs and symptoms resemble many others’. As of now, there exists no cure for the condition but its symptoms can be controlled with medical treatment.
The symptoms
The manifestation of Lupus is never exactly the same for two people though most people do experience it as episodes. These episodes are called ‘flares’ and the symptoms could possibly get real bad and then disappear altogether for a while. Lupus can set in slowly or suddenly and can be mild or severe. The symptoms of Lupus depends on the particular body system(s) affected as well. Here are some of the most common signs listed.
- Stiffness, pain and inflammation of the joints
- Fever and fatigue
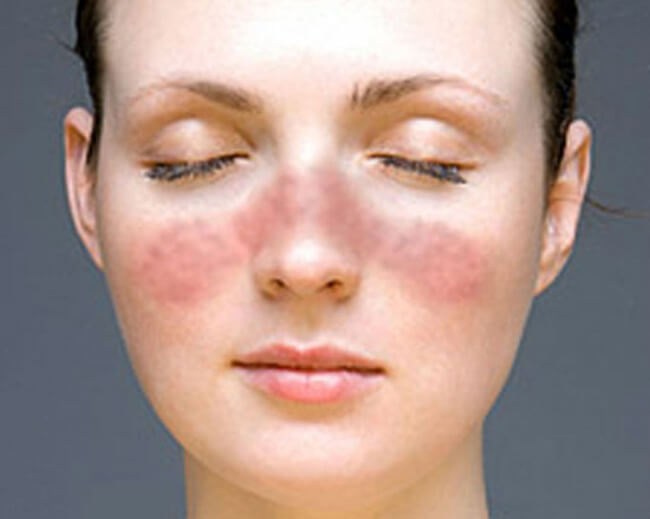
- A facial rash that covers only the cheeks and the nose’s bridge
- Lesions on the skin that worsen with exposure to the sun
- Shortness of breath
- Toes and fingers turn blue when stressed or exposed to cold.
- Causes and Triggers
It is most sensible to contact a doctor if one develops an unexplained rash, persistent fatigue and an ongoing fever. It is speculated that Lupus is triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Sunlight, infections and certain medications are known triggers. Developing an infection can possibly initiate Lupus and can also cause its relapse in the ones who’ve already experienced it.
More amongst women
Lupus is also found more in women and generally diagnosed in individuals between ages 15 and 40. Also, it is observed more amongst Asians, Hispanics and African Americans.
To know more about Lupus, please do feel free to get in touch with us.
Didn't find what you were looking for? Ask Dr Dixit your question and get answers within a day.
The information provided in Dr. Dixit's answer is for educational purposes only and is not intended to constitute medical advice. The information provided should not be relied upon as a substitute for consultations with a qualified health professional who may be familiar with your individual medical needs.

 09901890588
09901890588